
_776.jpg)
The Second Congo War, which lasted from 1998 to 2003, was the deadliest war since World War II. It was fought in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and involved a complex array of local and international forces. The war began as a conflict between the government of the DRC and various rebel groups, but eventually engulfed much of Central Africa as regional powers became involved in the conflict. At its peak, the war involved nine African countries and more than 20 armed groups. The catalyst for the war was the Rwandan genocide of 1994, when an estimated 800,000 people were killed. As a result of the genocide, many Rwandan refugees fled to the DRC and formed rebel groups to fight the government. The DRC government, led by President Laurent Kabila, responded to the rebel activity by launching a military offensive in 1998. This led to a regional conflict, with the Rwandan and Ugandan governments backing the rebel groups, and Angola, Namibia, and Zimbabwe supporting the DRC government. The war had devastating consequences for the people of the DRC. Over 5 million people were killed, and millions more were displaced. The country's infrastructure was destroyed, and economic activity ground to a halt. The war also led to a humanitarian crisis, as millions of people were left without access to food, water, or medical care. The conflict officially ended in 2003 with the signing of a peace agreement between the warring parties. However, the peace has been fragile, with sporadic violence continuing in many parts of the country. The legacy of the war is still felt today, with the DRC still one of the poorest countries in the world. The Second Congo War was a devastating conflict that highlighted the need for a strong international response to conflict in Africa.
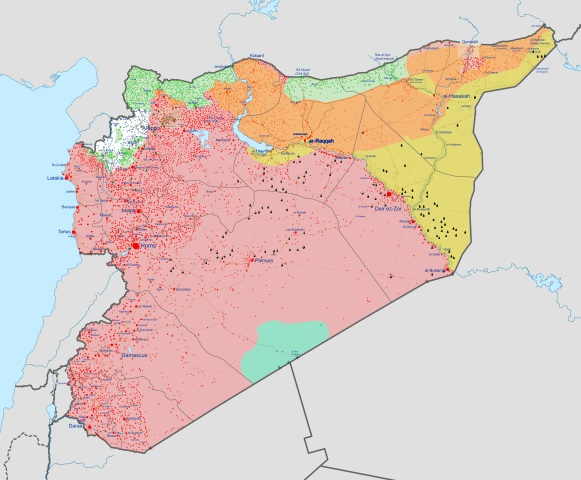
The Syrian Civil War, which began in 2011, is one of the deadliest wars in modern history. It is a complex multi-layered conflict, resulting from a combination of internal and external factors. It is a civil war between the government of Syria, led by President Bashar al-Assad, and various opposition factions, including the Free Syrian Army and several jihadist groups. The war has killed hundreds of thousands of people, displaced millions, and caused immense destruction throughout the country. The conflict began as an uprising against the regime of President Bashar al-Assad and his Ba’ath Party. The 2011 Arab Spring protests in Syria inspired a nationwide movement calling for political reform, but the Syrian government responded with a violent crackdown. The Syrian government used its military and security forces to violently suppress the protests, which resulted in a civil war between the government and rebel forces. The war has been characterized by extreme levels of violence. The government has been accused of war crimes, such as indiscriminate shelling of civilian areas and the indiscriminate use of barrel bombs. The use of chemical weapons and the targeting of hospitals and medical personnel have been reported. The conflict has resulted in a humanitarian crisis with millions of Syrians displaced both inside and outside of Syria. The war has also been characterized by a high level of foreign involvement. The United States, Russia, Iran, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and other regional actors have all been involved in the conflict. These actors have supported different sides of the conflict, providing arms, money, and political support. The war has damaged much of Syria’s infrastructure, resulting in the displacement of millions of Syrians and the destruction of many of its cities. The war has also had a devastating impact on the economy and on the Syrian people. The conflict has resulted in a high death toll, with estimates ranging from 400,000 to 600,000 people killed. The war has also left millions of Syrians displaced and in need of humanitarian aid. The Syrian Civil War is one of the deadliest wars in modern history. It has caused immense suffering and destruction, and its consequences are felt throughout the region. It is a multilayered conflict with many different actors, and its resolution will require a political settlement.
The Darfur Conflict is one of the deadliest wars in modern history. It began in 2003 when non-Arab rebel groups in Darfur, a region in western Sudan, began a rebellion against the Arab-led government in Khartoum. The government responded with a campaign of ethnic cleansing, targeting non-Arabs in the area. The government and its allied militias, known as the Janjaweed, have committed widespread atrocities, including murder, rape, and the burning of villages. The conflict has killed an estimated 300,000 people and displaced more than two million, making it one of the world’s largest humanitarian crises. The violence has also caused a massive refugee crisis, as hundreds of thousands of people have fled their homes in search of safety. The situation in Darfur has been further complicated by the presence of armed rebel groups, which have made the region increasingly unstable. In addition, the Sudanese government has used the conflict to further its own interests, providing weapons and support to the Janjaweed militias. The international community has responded to the crisis with a number of initiatives, including the deployment of a joint United Nations-African Union peacekeeping force in 2007. However, the conflict has continued to rage, and the humanitarian crisis has only deepened. The Darfur conflict is a complex and tragic situation, and a stark reminder of the devastating effects of war. The conflict has killed an estimated 300,000 people, displaced millions, and created a massive refugee crisis. Despite international efforts, the conflict is still ongoing, and the suffering of the people of Darfur continues.

The Iraq War, also known as the Second Persian Gulf War, is one of the deadliest wars in modern history. It began in March 2003 and lasted until December 2011. The war was fought between a U.S. led coalition and the Iraqi government forces of Saddam Hussein. The primary cause of the conflict was the United States' invasion of Iraq in 2003, with the stated goal of removing Saddam Hussein from power and disarming Iraq of weapons of mass destruction. The Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict that resulted in the death of thousands of coalition and Iraqi forces, as well as hundreds of thousands of civilians. The war also displaced millions of people from their homes, leading to a severe humanitarian crisis in Iraq and neighboring countries. The conflict was marked by a number of major battles, including the Battle of Fallujah, the Battle of Ramadi, and the Battle of Najaf. The war also saw the use of numerous sophisticated weapons, including air strikes, cruise missiles, and chemical weapons. Additionally, the war saw a large number of civilian casualties, as well as the destruction of many buildings and infrastructure. The Iraq War has been called one of the deadliest wars in modern history, with estimates of the death toll ranging from 150,000 to over one million. The total cost of the war has been estimated to exceed $2 trillion, making it one of the most expensive wars in history. Additionally, the war has had a major impact on the security and stability of Iraq and the region, with the ongoing conflict and instability in Iraq having significant implications for the region's security and stability.

The Afghanistan War, which began in 2001, is considered one of the deadliest wars in modern history. The war was initiated by the United States and its allies in response to the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks and in an effort to oust the Taliban regime and al-Qaeda from Afghanistan. The war has had a devastating impact on the people and landscape of Afghanistan, with the death toll running into the hundreds of thousands. The war began with the U.S. and its allies launching airstrikes against Taliban and al-Qaeda targets in October 2001. This was followed by a ground invasion by U.S. and coalition forces in December 2001. The Taliban was quickly ousted from power, but insurgency and terrorism have remained a constant threat since then. Over the years, the war expanded to include a variety of other actors, including the Afghan government, the Taliban, al-Qaeda, the Islamic State, and other foreign countries such as Russia and China. The war had a devastating impact on Afghanistan. According to the United Nations, more than 100,000 civilians were killed since 2001, and another 4 million displaced. The Taliban, al-Qaeda and other militant groups were accused of committing human rights abuses, including the use of torture and the recruitment of child soldiers. In 2018, the Taliban and the U.S. signed a peace agreement that was seen as a major step towards ending the conflict. The Afghanistan War ultimately ended with the overthrew the Islamic Republic by the Taliban in 2021, which re-established the Islamic Emirate.

The War Against Boko Haram is considered one of the deadliest wars in recent history. It began in 2009, when a militant Islamic group known as Boko Haram launched a series of attacks in northern Nigeria. The group, which is based in northeastern Nigeria, is believed to have ties to al-Qaeda and other extremist organizations. Over the years, the conflict has escalated and spread to neighboring countries such as Cameroon, Chad, and Niger. The group has used guerrilla tactics to launch attacks on military and civilian targets, including schools and churches. They also kidnapped hundreds of civilians, including hundreds of schoolgirls in April 2014. The Nigerian government has responded to the group's actions with a military campaign. The government has deployed troops to the affected areas and has conducted air strikes against the group. However, despite these efforts, Boko Haram has been able to maintain control over large parts of the region. The conflict has resulted in an estimated 20,000 deaths and more than two million people being displaced from their homes. It has also taken a heavy toll on the economy, with the World Bank estimating that the region's GDP has declined by as much as 25%. The war against Boko Haram is an international problem, and the United Nations has been involved in attempting to resolve it. In 2015, the UN Security Council unanimously adopted Resolution 2178, which called for international action to address the conflict. In 2016, the African Union launched a regional task force to help combat the group. The conflict shows no signs of abating, and it remains one of the deadliest wars in recent history. While the Nigerian government and international organizations have made some progress in containing the group, it continues to pose a significant threat to the stability of the region.
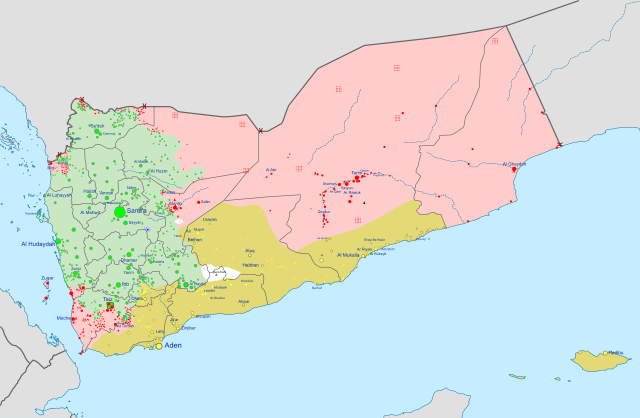
The Yemeni Civil War is an ongoing armed conflict in Yemen that began in 2015 between the Houthi movement, a Zaidi Shia-led religious-political insurgent group, and the Yemeni government of President Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi, backed by a Saudi-led coalition of Arab states. The conflict has resulted in one of the deadliest wars in recent history, with estimates of over 100,000 casualties and more than 3 million displaced persons. The war began in 2015 when the Houthis, a Zaidi Shia-led insurgent group, began an uprising against the government of President Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi, claiming to be the legitimate leaders of Yemen. In response, the Saudi-led coalition, backed by the United States, launched an extensive air campaign aimed at restoring the Hadi-led government. This quickly escalated into a full-scale civil war, with multiple sides fighting for control of the country. The war has seen significant civilian suffering due to the extensive use of air strikes and ground battles. Thousands of civilians have been killed or maimed by airstrikes, and hundreds of thousands more have been displaced by the fighting. The conflict has also caused a major humanitarian crisis in the country, with over 17 million people in need of food and medical aid. The lack of access to food and medical supplies has caused a famine and a cholera outbreak, exacerbating the suffering of the Yemeni people. The war has also seen significant political upheaval, with several different factions vying for control. In 2018, the Houthis and the Saudi-led coalition signed a United Nations-mediated ceasefire agreement, but the conflict has continued. In 2020, the UN-backed Yemeni government and the Houthi movement agreed to a new power-sharing agreement, but the details of this agreement have yet to be fully implemented. The Yemeni Civil War is one of the deadliest wars in recent history, and it has caused immense suffering among the Yemeni people. The conflict has been marked by extensive use of air strikes, ground battles, and political upheaval, with multiple sides vying for control of the country. The war has caused a major humanitarian crisis, with millions in need of food and medical aid.

In 2014, the conflict began with Russia's annexation of Crimea. Following the ousting of Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych, Russia capitalized on the political turmoil and deployed its military forces to occupy Crimea. A hastily organized referendum was held in Crimea, resulting in the majority of the population voting in favor of joining Russia. The occupation of Crimea was condemned by several countries, which deemed this action as a violation of Ukraine's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
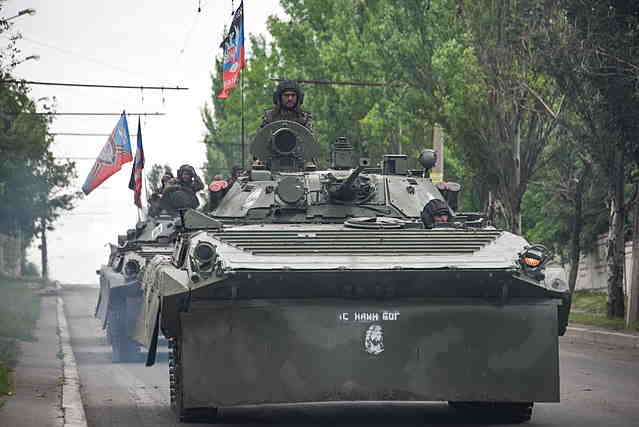
After the annexation of Crimea, areas in eastern Ukraine (especially in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions) saw the emergence of pro-Russian separatist movements. These separatist groups, with alleged support from Russia, declared independence and sought to establish self-proclaimed republics. The Ukrainian government responded by launching a military operation to regain control over the separatist-held territories.
The fighting intensified throughout 2014 and into subsequent years, resulting in a significant loss of life and the displacement of thousands of people. Ceasefire agreements were attempted, including the Minsk Protocol and the Minsk II Agreement, but their implementation proved challenging, with numerous violations by both sides.
In 2022, the conflict witnessed a significant escalation. In the beginning of 2022 Russia amassed a large number of troops near the Ukrainian border, raising concerns of a potential invasion. In February, Russia launched a full-scale invasion into Ukraine, with its forces crossing the border and advancing into Ukrainian territory. The invasion led to intense fighting and a humanitarian crisis, as cities and towns were heavily impacted by the conflict.
The international community strongly condemned Russia's actions, and economic sanctions were imposed on Russia by various countries. Ukraine appealed for support from its allies and received military assistance and diplomatic backing.
Efforts to negotiate a ceasefire and a peaceful resolution to the conflict have continued, with negotiations taking place in various forums. The conflict remains unresolved, with both sides holding firm positions and a volatile situation on the ground.