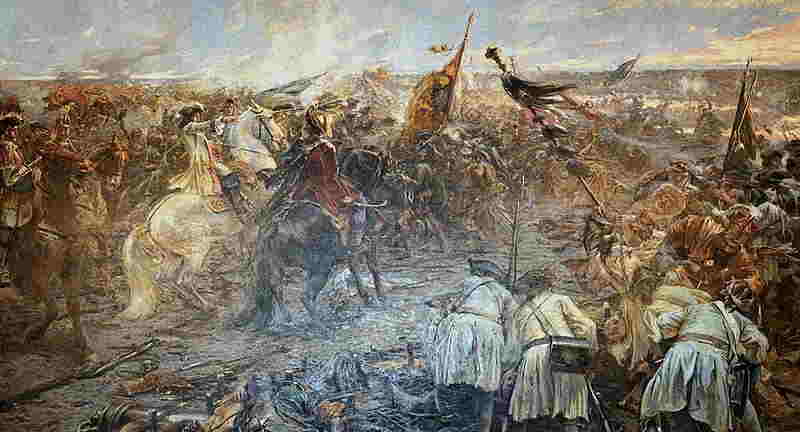


The Battle of Zenta, fought on September 11, 1697, was a decisive victory for the Ottoman Empire over the Holy League of Austria, Poland, and Venice. This battle had far-reaching consequences for the shape of the modern world. First, the Ottoman Empire gained a major strategic advantage in the region, which allowed them to take control of much of Eastern Europe. This included parts of Hungary, Serbia, and Romania, as well as other areas of the Balkans. As a result, the Ottoman Empire was able to expand its influence and power well into the 19th century. Second, the victory at Zenta enabled the Ottoman Empire to become an even more powerful international player. This was due to their improved military capabilities and the increased resources that they gained from the territory they acquired. This allowed them to become more involved in international affairs and play a more prominent role in global politics. Third, the Battle of Zenta also had a significant impact on the religious landscape of Europe. The Ottoman Empire was a Muslim state and they were able to spread their faith in the areas they conquered. This eventually led to an increase in the number of Muslims in Europe and the spread of Islam into the continent. Finally, the Battle of Zenta also had an influence on the course of European history. The Ottoman Empire was able to gain control of many areas of Eastern Europe and this ultimately led to their decline in the 19th century. By establishing their control over the region, the Ottomans were able to prevent the spread of other empires, such as the Austrians, into the area. This allowed other nations to develop in a more independent manner and ultimately led to the formation of the modern nation-states of Europe. Overall, the Battle of Zenta had a major impact on the modern world. It allowed the Ottoman Empire to expand their influence and power in the region, which in turn enabled them to become a major international player. In addition, it also had a significant impact on the religious landscape of Europe and the course of European history. Thus, the Battle of Zenta has certainly had an enormous influence on the shape of the modern world.
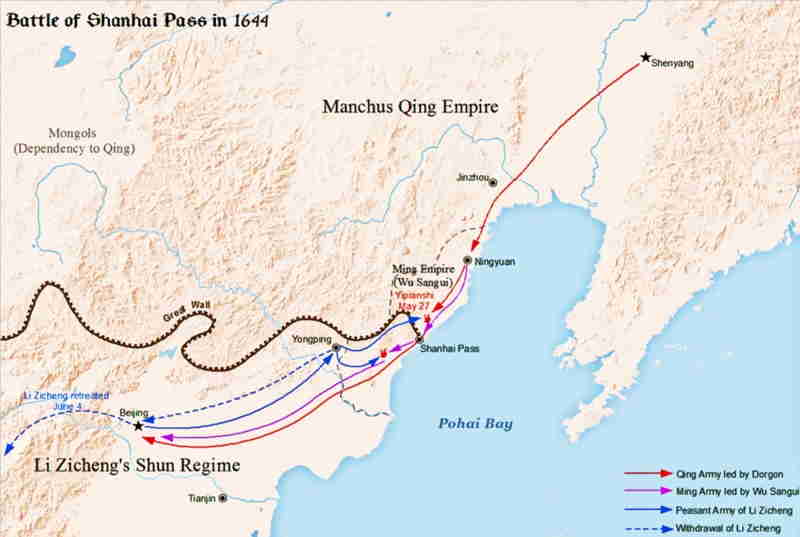
The Battle of Shanhai Pass is a pivotal turning point in Chinese history, and its repercussions can still be felt today in the modern world. In 1860, the Qing Dynasty of China was at a crossroads. The Taiping Rebellion had been raging for almost a decade and had brought the nation to its knees. To protect the country from further destruction, the Qing rulers decided to seek assistance from the foreign powers of the West. However, the Western nations refused to help unless the Qing government agreed to open certain ports to foreign trade. This included the city of Shanhai, which was the gateway to the north and the most important port for trade in the region. The Qing rulers, desperate to protect their nation, agreed to these terms and opened Shanhai to foreign ships. In response, the Western powers sent a fleet of warships to the city in an attempt to secure the port and open it up to foreign trade. In the ensuing battle, the Qing forces were victorious and managed to successfully protect the city. This victory was a major turning point in Chinese history and set the stage for the modernization of the country. The success of the Qing forces at the Battle of Shanhai Pass was a direct result of their reliance on new technologies, such as cannons and rifles, and their willingness to use modern tactics and strategies. This was a key factor in the victory, and it laid the foundation for the modernization of China in the years to come. The modern world has been greatly shaped by the events of the Battle of Shanhai Pass. By making use of modern weapons and tactics, the Qing forces were able to protect their nation and open it up to foreign trade. This allowed for the modernization of the country, which helped to propel it into the world economy and set the stage for the economic growth and development that China has seen over the past few decades. Without this pivotal moment in Chinese history, the world would look very different today.

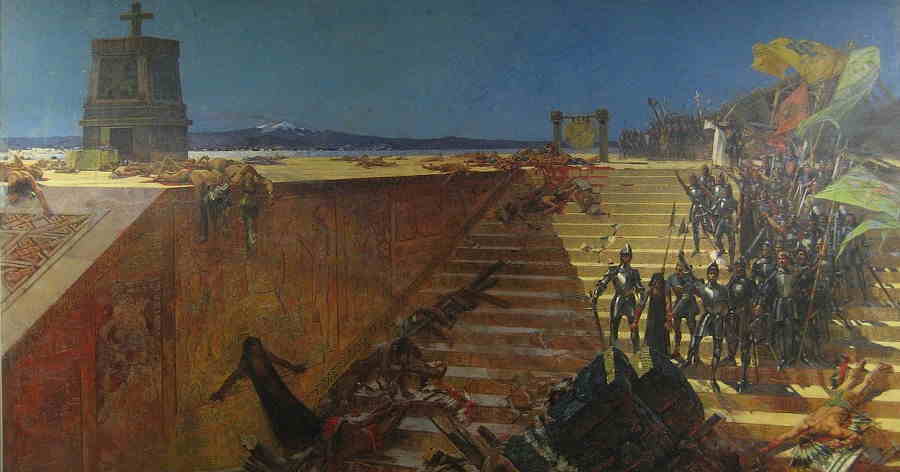
The Siege and Fall of Tenochtitlan was a pivotal event in world history that changed the shape of the modern world. It was the climax of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, which began in 1519 when Spanish conquistador Hernan Cortes arrived in the region. The Spanish were able to take advantage of the internal divisions among the Aztec people, as well as their technological superiority, to gain control of the region. In 1521, after a series of defeats by the Spanish forces, the Aztecs were forced to surrender and the city of Tenochtitlan was taken. The fall of Tenochtitlan marked the beginning of Spanish colonization in the New World and the end of the Aztec Empire. The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire had a major impact on the shape of the modern world. It marked the beginning of European colonialism in the New World, a legacy that has had far-reaching consequences. The Spanish conquest also resulted in the spread of Christianity throughout the region and the introduction of the Spanish language, which is still the official language in many countries in the Americas. The fall of Tenochtitlan also had a major impact on the indigenous peoples of the region, as many were displaced and their traditional way of life was disrupted. In addition to the political, religious and cultural changes that resulted from the fall of Tenochtitlan, it also had a major economic impact. The Spanish conquest opened up the region to trade with Europe, leading to increased wealth and prosperity for the region. This, in turn, led to the development of new industries and the growth of major cities. The Siege and Fall of Tenochtitlan, therefore, changed the shape of the modern world in a variety of ways. It marked the beginning of European colonization in the New World and the introduction of Christianity, the Spanish language and new economic opportunities. Its legacy continues to be felt today and its impact can still be seen in the political, religious, cultural and economic life of the region.
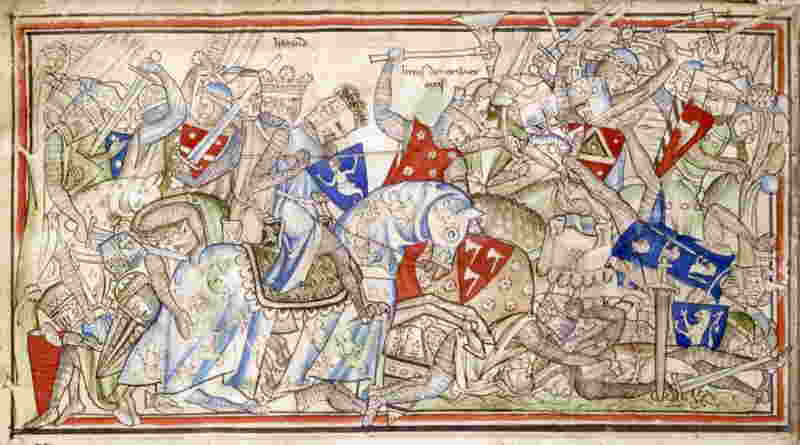

The Battle of Stamford Bridge, fought in 1066, was the last major battle of the Viking Age and was a decisive victory for the English. It marked the end of Viking invasions of England and the effective decline of Viking power in Northern Europe, ushering in an era of Norman rule in England and ultimately the formation of the United Kingdom as a whole. Its effects would be felt for centuries. By ending Viking rule in England, the Battle of Stamford Bridge allowed the Normans to firmly establish their rule over the island, leading to the spread of their culture and language throughout the British Isles. The Normans also introduced many of the laws and traditions which still influence the United Kingdom today, such as trial by jury, the establishment of the feudal system, and the use of Latin as an official language. The battle was also a major factor in the development of the English language. It was during the Norman period that Old English and Old Norse combined to form what is now known as Middle English, which was the language of the English people until the 14th century. This mix of languages had a lasting effect on the English language and its development into modern English. The Battle of Stamford Bridge also had a significant impact on the development of Europe. By ending Viking rule in England, the Normans were able to expand their power into other parts of the continent, eventually leading to the establishment of the Holy Roman Empire. This empire, which lasted for over a thousand years, was a major political and cultural force in Europe throughout the Middle Ages and beyond. The Battle of Stamford Bridge was thus a pivotal moment in European history. By ending Viking rule in England, it allowed for the Normans to establish their own rule and for the spread of their culture throughout Europe. This, in turn, led to the formation of the Holy Roman Empire and the development of the English language. All of these factors have had a profound effect on the shape of the modern world.

The Battle of Achelous was fought between the Greek and Persian armies in 480 BC. The battle was fought in the valley of the Achelous River in northern Greece, and was part of the Greco-Persian Wars. The Greek forces, led by the Athenian general Themistocles, were victorious, decisively defeating the Persian forces and ending their threat to the region. The victory at the Battle of Achelous had far-reaching implications for the ancient world. Most notably, it marked the end of the Persian Empire’s attempts to expand its control into the Mediterranean region and Europe. As a result, the Greek city-states were able to maintain their independence and autonomy. This allowed them to develop their own form of democracy, which would later become the foundation for modern democracies around the world. The Battle of Achelous also demonstrated the importance of naval power in warfare. The Greeks were able to use their superior naval forces to outmaneuver the Persians and gain a decisive victory. This was a lesson that many other countries would later take to heart, as naval power would become a major factor in many conflicts in the centuries that followed. The victory at the Battle of Achelous also signaled a shift in the balance of power in the ancient world. It cemented the supremacy of the Greeks over their Persian rivals and demonstrated the strength of the Greek polis, or city-state system. This would become the foundation for the rise of the Classical Age of Greece, which would have a profound influence on Western civilization. Ultimately, the Battle of Achelous changed the shape of the modern world in many ways. It ended the Persian threat to the region, allowed the Greek city-states to maintain their independence, and shifted the balance of power in the ancient world. It also showed the importance of naval power in warfare and provided the foundation for the Classical Age of Greece. All of these developments would have a lasting impact on the modern world, making the Battle of Achelous one of the most important events in the history of mankind.

The Battle of São Mamede is considered one of the most important battles in the history of the modern world. It is an event that has had a lasting impact on the world and changed the shape of the modern world. The battle was fought between the forces of Afonso Henriques and the forces of the Moors, led by Almoravids, in 1128 CE, in the São Mamede region of Portugal. The victory of Afonso Henriques was decisive, with the Moors being routed and most of their leaders killed. The victory of the Portuguese forces allowed Afonso Henriques to become the first King of Portugal, and laid the foundation for the eventual formation of Portugal as an independent nation. The significance of the battle of São Mamede lies in its establishment of the Portuguese nation and its subsequent role in the European and world stage as a powerful trading and military force. With the victory of Afonso Henriques and the formation of Portugal, the country became a major power in the Mediterranean and a major trading partner with the countries of North Africa and the Middle East. The Portuguese Empire would become one of the most powerful empires in the world for the next several centuries, with its influence stretching from the Americas to Africa and Asia. In addition to its political and economic significance, the Battle of São Mamede also had a lasting cultural impact. The victory of the Portuguese over the Moors allowed Portugal to become an important center of Christian culture and faith, and the Portuguese language and culture would spread around the world with the Portuguese exploration and colonization of the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Overall, the Battle of São Mamede has had a lasting impact on the modern world. It established Portugal as an independent nation and a major power in the Mediterranean and Europe, and its influence and exploration would spread Portuguese culture and language around the world. It is an event that has shaped the modern world in many ways.
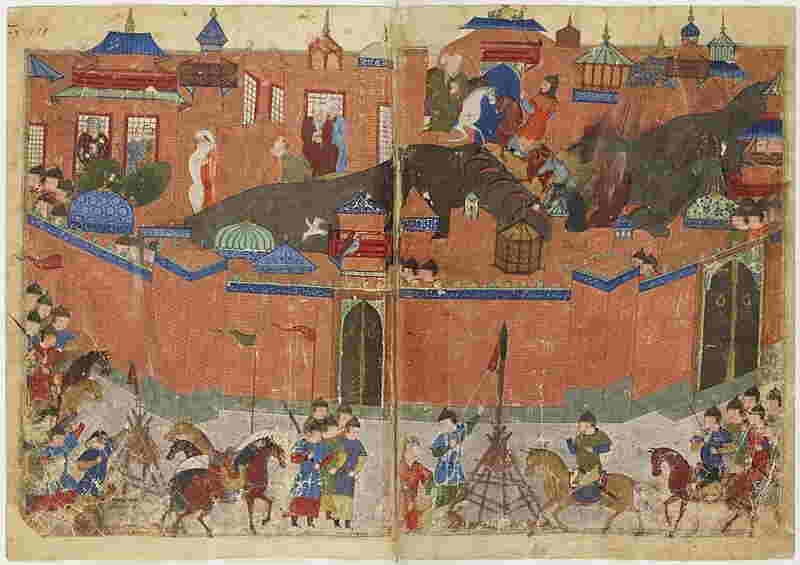

The Siege of Baghdad in 1258 was a critical turning point in world history, reshaping the political and cultural landscape of the Middle East, and ultimately the world. The siege marked the end of the Abbasid Caliphate, which had been the most powerful Islamic empire since the death of the Prophet Muhammad. This event opened the door for the Mongol invasions of the Middle East and the eventual creation of the Ottoman Empire. The Mongol conquest of the Middle East had a profound impact on the region. The destruction of Baghdad and its famous libraries, along with the massacre of its population, was a major blow to Islamic civilization. This loss of knowledge and culture was a major setback for Islamic science, philosophy, and art. The destruction of Baghdad was also a major blow to the Islamic Golden Age, which had been a period of stability and cultural achievement for the Islamic world. The Mongol conquest of the Middle East also had an impact on the wider world. The Mongols created a vast trade network, connecting East and West. This allowed for the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture. This increased contact between the East and the West eventually led to the European Renaissance and the Age of Exploration. The Siege of Baghdad has also had an effect on the modern Middle East. The Mongol conquest of the region created a power vacuum, which was filled by the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman Empire eventually dominated the region for centuries, and the legacy of the Ottoman Empire can still be seen in the political and social landscape of the Middle East today. In conclusion, the Siege of Baghdad has had a profound effect on the modern world. It marked the end of the Abbasid Caliphate, which had been the most powerful Islamic empire for centuries. It also opened the door for the Mongol invasions of the Middle East, which reshaped the region politically and culturally. These events also had an effect on the wider world, leading to increased contact between East and West and eventually the European Renaissance. Finally, the Ottoman Empire filled the power vacuum left by the Mongol conquest, creating a legacy that can still be seen in the modern Middle East.

The Battles of Hakata Bay, fought in 1274 and 1281, were two of the most important battles in the history of Japan. The battles marked the end of the Kamakura Shogunate and the beginning of the Muromachi Period. The battles also marked a shift in power from the Samurai and their feudal system to the imperial court in Kyoto. The first battle, fought in 1274, saw the Mongol forces of Kublai Khan defeated by the Japanese forces led by samurai Kusunoki Masashige. This was the first time a foreign invader had been successfully repelled by a Japanese army, and it marked a significant shift in the balance of power in the region. The second battle, fought in 1281, saw the combined forces of the Kamakura Shogunate and the imperial court in Kyoto defeat the Mongol forces of Kublai Khan. This battle effectively ended the Mongol invasion of Japan and marked the end of the Kamakura Shogunate. The battles of Hakata Bay changed the shape of the modern world in a number of ways. First, they marked the beginning of a new period of Japanese history known as the Muromachi Period. This period saw the emergence of the samurai class, the rise of merchant and farming communities, and the introduction of new cultural and religious practices. Second, the battles of Hakata Bay demonstrated the strength of the Japanese military and their ability to resist foreign invaders. This had a tremendous impact on the global perception of Japan, and it helped to establish the country as a world power. Finally, the battles of Hakata Bay helped to establish the concept of a unified Japan. By defeating the Mongol forces, the Japanese forces demonstrated that the various provinces of Japan could be united under a single ruler. This concept would later become the basis of the modern nation of Japan. In conclusion, The Battles of Hakata Bay were two of the most important battles in Japanese history. They marked the end of the Kamakura Shogunate and the beginning of the Muromachi Period. They also demonstrated the strength of the Japanese military and helped to establish the concept of a unified Japan. As such, they had a tremendous impact on the shape of the modern world.

The Battle of La Forbie, which took place in 1244, was an important turning point in world history. It was fought between the armies of the Crusaders and the forces of the Ayyubid Sultan al-Kamil. The battle saw one of the most decisive victories of the Crusaders in the Holy Land, and it marked a turning point in the struggle for control of the region. The victory at La Forbie marked the end of the Ayyubid dynasty’s control over the Middle East. It also brought an end to the Muslim presence in the region, and it allowed the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem to become firmly established. This victory helped to ensure that Christianity would remain the dominant religion in the region. The victory at La Forbie also helped to shape the modern world. It was the first major victory in the Crusades, and it demonstrated the power of the Christian armies in the region. This victory helped to establish the concept of a “Christian Holy Land”, and it laid the foundation for the modern state of Israel. The victory at La Forbie also helped to shape the modern geopolitical landscape. The fall of the Ayyubid dynasty helped to create a balance of power between Christian and Muslim forces in the region. This balance of power helped to prevent further conflict between the two sides, and it allowed for the development of more peaceful and cooperative relationships between them. The victory at La Forbie also helped to shape the modern world in other ways. The victory boosted morale in both the Christian and Muslim forces, and it helped to create an atmosphere of tolerance and understanding between them. This atmosphere of tolerance helped to create a more stable and peaceful environment, which in turn helped to foster the development of trade and other forms of economic growth. The Battle of La Forbie, then, is an important event in world history that helped to shape the modern world in many ways. From helping to create a balance of power between Christian and Muslim forces to boosting morale and fostering economic growth, this battle has had a lasting impact on the world we live in today.

The Battle of Didgori, fought in 1121, was a decisive victory for the Georgian army against the Seljuq forces, which had conquered much of the Caucasus region. The victory was a major turning point in Georgia’s history, as it marked the first time that a Christian kingdom had successfully repelled an Islamic invasion. The battle also had far-reaching implications for the shape of the modern world. The Battle of Didgori demonstrated the strength of the Georgian army and helped to establish it as a major power in the region. This in turn helped to protect the Christian world from further Islamic expansion and laid the groundwork for the eventual establishment of the Eastern Orthodox Church as the primary religious force in the Caucasus. In addition, the battle was a major factor in helping to break up the Seljuq Empire, which had been a major regional power during the Middle Ages. The victory at Didgori also had a significant impact on the development of military tactics. Prior to the battle, the Georgian army had relied heavily on cavalry and had little experience with infantry tactics. However, the Georgians were able to successfully employ infantry tactics during the battle, which allowed them to outmaneuver and outlast the Seljuq forces. This innovation in tactics was then adopted by other European armies, leading to the development of modern infantry tactics and strategies. Finally, the victory at Didgori helped to create a sense of national pride and identity among the people of Georgia, which has remained strong to this day. This national pride has been a major factor in helping to keep the country unified and stable through many periods of turmoil and conflict. In conclusion, the Battle of Didgori had a profound impact on the shape of the modern world. The victory helped to protect the Christian world from further Islamic expansion, break up the Seljuq Empire, and develop modern infantry tactics. It also strengthened Georgia’s national identity and helped to ensure its continued stability. Thus, the Battle of Didgori was a crucial event in the history of the world.